As we live our lives more and more online confidence men have worked to take digital scamming to a whole new level. From trying to get us to claim inheritances from long lost, never heard of them relatives to sending past due invoices for something you might have signed up for to intercepting communications and impersonating customer service agents to steal your information.
What is a phishing scam?
A phishing scam is an online targeted attack on consumers that attempts to acquire their personal data by creating emails, text messages, social media, or phone calls that appear legitimate. Here are a handful of the most common ones:
Types of scams:
- Pharming: Pharming is a two-step process where an attacker installs malicious code on your computer to direct their victim to a spoof website where they try to steal credentials and other data.
- Website spoofing: Attackers will use branding from popular and trusted companies to lull web users into a false sense of security. They will use everything from logos to content and product lists to domain names to make sites appear to be the official website of a brand to get you to provide your user credentials or other sensitive information.
- Angler phishing: Scammers will pose as customer service reps on social media pages to trick their customers into giving login information.
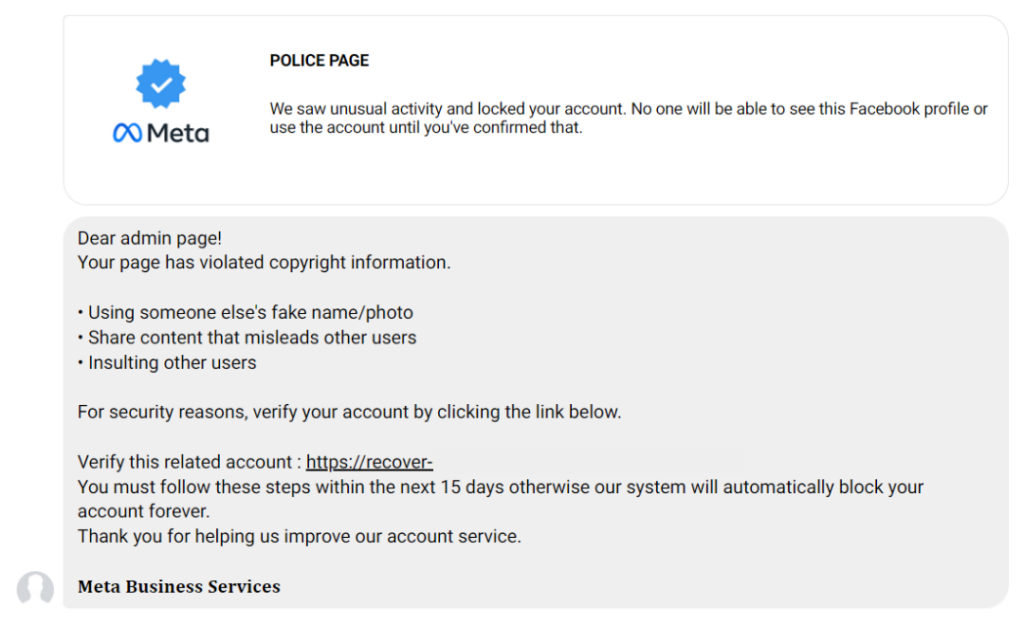
- “Spear phishing”: This type of attack tries to get access to a computer system using messages that mention current events, or references financial or important documents, or a business process to make a user feel they are being helpful in completing a task. The goal is to obtain banking information, usernames & passwords, or have funds wired.
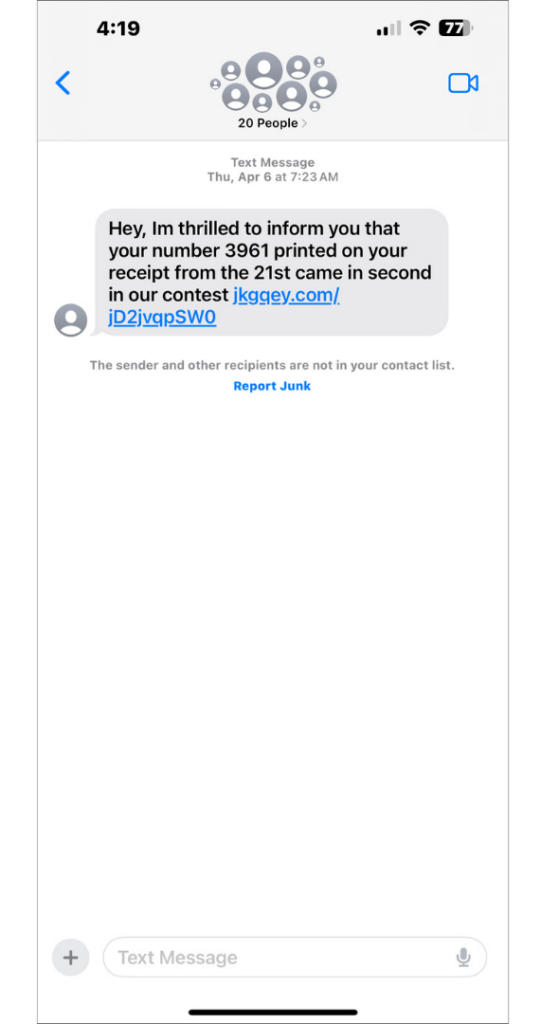
- Smishing: Smishing – a combination of SMS and phishing – uses fake text messages to trick people into downloading malware, sharing personal information, or sending money to the perpetrators.
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack: Cybercriminals intercept communications between a customer and the customer service representatives to manipulate customers into sharing sensitive information. From creating public wifi networks to IP address and website spoofing, they use any means to intercept financial data and other information.
How to Recognize Phishing
“Knowledge is power” is a popular saying for a reason. The more you know about various phishing scams, the better you’ll be able to protect yourself. Knowing what a phishing scam looks like, from the verbiage to font choices – yes, even changing fonts can manipulate you into making a costly mistake – is one way to protect yourself.
As a business owner, you can help your customers know what they can and should expect from you.
- What your website and brand design looks like
- What platforms you use to send certain information, like invoices
- How you will communicate with them (email, text message, social media messaging)
- What your email address structure is
- What you will and won’t offer to your customers (i.e. gift cards, free money, etc)
Being knowledgeable is also recognizing when something isn’t quite right. It’s about being familiar enough with company logos, email address formats, and signature lines will help know whether an email is valid.
Large companies have marketing guidelines for every piece of communication that goes out to the world. They are exacting and all employees are required to follow them. They also standardize how they communicate with customers. Do they email? Do they text? Do they slide into user’s DMs, in the case of social media? Before clicking on any links, read emails from top to bottom.
Let’s analyze a scam email
In the image to the left, there are three key things to notice that make it a clear giveaway as a phishing email.
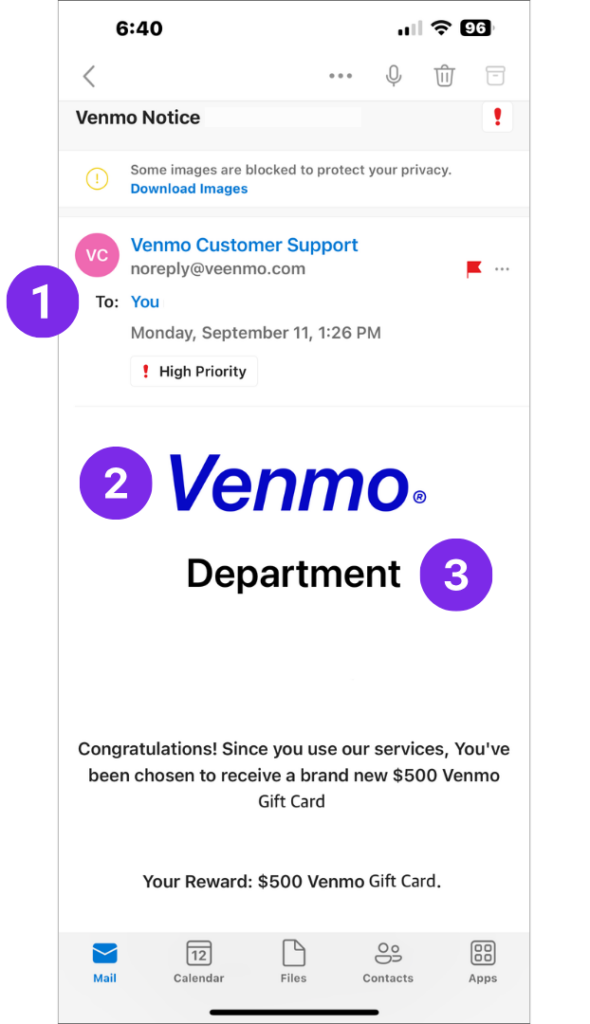
1. First thing to notice is the sender’s email: [email protected]. The domain is misspelled.
2. It’s easy to get distracted by the large Venmo logo in the center of the email. If you pay close enough attention, however, you will notice that whoever created this email didn’t use the correct font for the logo.
3. Finally, the inclusion of the word “Department” under the logo is also cause for concern. What department? Venmo isn’t a department; it’s a company.
From these three signs alone, you know it is a phishing email and you should avoid engaging with this email.
The image to the below is a legitimate email from Venmo, using the correct email address, logo font, and an on brand, carefully crafted message to its consumers about giving a gift through their app.

How to Protect Yourself
To protect yourself and your business from natural human insecurities, you have to be proactive. Phishing scams prey on our weaknesses and insecurities. No one wants to have outstanding bills; no one wants to disappoint their boss; and everyone wants free money.
Train yourself: To protect yourself, you need to train yourself how to detect phishing scams. The example above is just one attempt at phishing. Familiarize yourself with other types of scams. Be knowledgeable enough about the brands you interact with to recognize when something is off with a message. The more you know, the more confident you will be when your instincts tell you something is off.
Install security software: The first line of defense is having security software installed on your and your employees computers. They will detect any attempts to install malware onto your devices and thwart it.
Update and Backup Devices Regularly: Phishing scams’ main goal is to take your information by any means necessary. In some cases, that can end with you losing all your information. Staying on top of software updates also keeps your devices safe as programmers are constantly making tweaks and fixing bugs to improve security and performance. Backing up your data on an external hard drive or the cloud will ensure that you have everything you need in case of an attack.
Implement Password Policies: Setting expiration dates and having requirements for passwords is another way to ensure passwords are strong and if any are compromised that they are regularly updated in order to protect devices and information.
Multi-factor Authentication: Using multi-factor authentication apps like Google Authenticator adds one more layer of security like a texted or random generated number. This is a very strong form of protection that will give you time to reset/change passwords if one gets compromised.
Pay attention to Email Content: If you receive an email that seems too good to be true – a large inheritance from a stranger in Australia or your boss asking for help buying a gift for the entire staff – or makes you nervous – overdue invoices for a service that you have, it probably is and you should delete it without engaging any further or check your accounts. Don’t ever click on suspicious links as that can trigger malware or cloning software to copy your information. Visit company websites by typing the link in yourself and logging in independent of the email.
Report Bad Actors: Preventive measures are great, but you can always go one step further and report the individuals trying to take advantage of you. While you won’t have a face or a name, digital crimes can be tracked and shutdown by professionals. This not only keeps you from being attacked again – at least by this person – and prevents them from attacking anyone else.
Being informed and being proactive are the two best ways to protect yourself from phishing attacks . Because of how integrated the online world has become with the real world, we have to be extra cognizant and vigilant about what we share, how we share it, and who we share it with.

